Small Start-up Business Project Management
Abstract
This article introduces how business starters can use project management to start up their small businesses. First we identify the minimal set of tools that is good enough for small business starters to use. Then we map project management tools to our business start-up process to identify opportunities we can exploit project management. Finally we can create or borrow tools that adhere to the process mapping. There are lots of work can be done in the future for this program, including educating the public basic project management concepts, introducing or creating project management tools to the user and ensure they develop a habit of using them.
Introduction
Entrepreneurs and small businesses are important to economy. This article is to determine what project management skills and tools suitable are optimal for small business starters to ramp up business, manage operations, deliver tailored or bespoke products to customers, and manage innovation and growth. We assume readers have basic knowledge of project management although we will ultimately hope broader audience can benefit from using lite project management skills. This may also be a starting point for a program introducing project management to small and micro businesses, or even to the wider public.
The ultimate goals for the program may be:
- Introduce project management to the wider public, start with small business owners
- Start-up business users can simplify and manage their life and tasks using tools or knowledge provided
- Enable small business owners to be more organized and systematic so as to reduce stress and anxiety
This article refers to two literature sources, one is a paper from Turner (Turner, 2011) in PMI Journal, and another is the small start-up business program from a College in Ontario, Canada.
The problem statement and scope of this article would be:
- To what extent do small micro business use project management both in their mainline business and to manage innovation and growth?
- What elements of the project management are important for small micro business?
- A Business Start-up Process
- How project management fit, map, or morph into Business Start-up Process
The following would not be in scope:
- Details of innovation project management.
- Lower Level Description of tools and content generated from the morph of project management and business start-up process.
- Project Management ABCs
- Operation Management and Project Management Morphing
Strategy
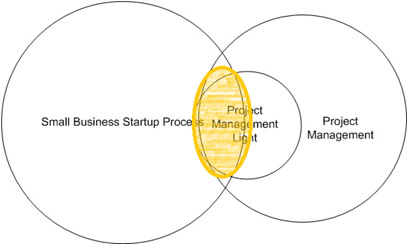
To develop the skillsets, knowledge, and tools, first we will define Project Management Light (PML), derived from PMBOK referencing Turner`s literature. Then we will define a Small Business Start-up Process, for this paper we use the process used by Ontario Self Employment Benefit Program. Afterwards, we will start morphing some of them (demonstrated by the orange area). There are many different ways of morphing the activities and process. We will use table mapping methods commonly used in business and system analysis to start to complete the scope of this article.
Project Management Lite (PML) (Turner, 2011)
Characteristics
- We would expect simplified project planning and control systems, with simplified reporting mechanisms.
- We would not expect to see them adopting some of the standard methodologies.
- We also expect to see people fulfilling several roles on projects, especially in smaller companies.
- Microsized companies do not employ specialist project managers, and so projects are managed by people with other primary roles, and small and micro-sized companies do not tend to use the recognized tools and techniques of project management.
- uses laissez-faire management and egoless team structures
- Use of project management
- Operations management (This is very important but details about project and operation management morphing will be out of scope)
- Innovation and growth: (Innovation Process is too complicated to be in scope in this article. Also not every start-up business innovates. We will talk about Innovation Process Project Management in another article. However for the growth, we will talk about Business Start-up Process.)
- Lite project management
PMLite Content (Turner, 2011)
| PMBOK practices | ✔ | Remarks |
| Client requirements | ✔ | The need to define client requirements as an essential first step. Communication Management |
| Road map or milestones | ✔ | High level schematic plan. to provide an overall vision of how the project would be completed |
| Work breakdown or activity lists | ✔ | Define the activities required to do the work |
| Agile or scrum | Uses laissez-faire management and egoless team structures; also requires all the team members to be able to do all the work, so it requires homogeneous work and homogeneous teams. | |
| Responsibility assignment matrix | × | they don’t need that formality |
| Scope and resource schedule | ✔ | Simple form of scope or resource schedule. Some have a simple resource schedule, with dates against their activity list. Others also have a resource schedule with dates against the involvement of named resources. |
| Team building | × | No Formal Team building is needed. |
| Risk and issue management | ✔ | Need risk management. The most important project management functionality they applied. |
| Commercial project management | ✔ | Simple appraise the value of projects, Buy or hire, Buy-or-do it yourself, contract management. |
| Domain knowledge | ✔ | Basic domain knowledge in their work. |
| Microsoft project | × | Too complicated. Perhaps Excel is good enough |
| Project Office | × | No Need |
| Cost management | ✔ | Very Simple Financial Cost, Sales and Tax Tracking. No Earned Value Analysis |
| Quality management | × | Use Manage Client Requirement |
| Integration management | × | No Need |
| Life-cycle and stage gates | × | No need |
| Program and portfolio management | × | No need except for innovation. Will talk about Innovation in other paper |
The above table shows what elements of the project management are important for small micro business.
Company Profile
After the elements of PM Lite are identified, we develop a company profile. This company profile includes the elements they will be using in the business start-up process that is specific to the company.
| Company: TSE and TSE business and Technology Consulting |
| ■ requirements analysis ■ milestone planning ■ work breakdown and activity lists ■ responsibility assignment matrix ■ work schedules (and checklist and Gantt charts) ■ PM software for work scheduling and control (micro-soft project) ■ PM software for resource scheduling (but not resource schedules per se) ■ Kick off meetings ■ Risk management (but not issue management) ■ Scope management ■ Cost management ■ Commercial management |
Project Management and Business Start-up Process
SO how we can tie Business Start-up Process and Project Management Together? How we are going to use project management techniques to manage our business start-up process?
There are at least two dimensions I can think of in terms of mixing them two together. One is Business Start-Up as a project; another is Business Start-Up Process Items and PMLite mapping. For the first one, it is to put the whole business startup process into a master project management schedule. The second one is the for each item inside the process, identify PM concepts or items that would be useful to help executing the tasks. Some of the items can me a project itself.
Business Start-Up as a Project
For this example, we choose the Microsoft project start up template as an example to illustrate how we can put business start-up process into a Gannt Chart, Schedule or work breakdown structure. This process has a lot of action item executable to start up the business. Each item has duration, start date, end date, resource, dependencies etc.
|
1 |
Phase 1 – Strategic Plan | 23 days | 01/01 | 02/02 | ||
|
2 |
Self-Assessment | 3 days | 01/01 | 05/01 | ||
|
3 |
Define business vision | 1 day | 01/01 | 01/01 | Manager | |
|
4 |
Identify available skills, information and support | 1 day | 02/01 | 02/01 | 3 | Advisor, Manager |
|
5 |
Decide whether to proceed | 1 day | 05/01 | 05/01 | 4 | Manager |
|
6 |
Define the Opportunity | 10 days | 06/01 | 19/01 | ||
|
7 |
Research the market and competition | 1 day | 06/01 | 06/01 | 5 | Advisor |
|
8 |
Interview owners of similar businesses | 5 days | 07/01 | 13/01 | 7 | Owners |
|
9 |
Identify needed resources | 2 days | 14/01 | 15/01 | 8 | Advisor, Peers |
|
10 |
Identify operating cost elements | 2 days | 16/01 | 19/01 | 9 | Accountant |
|
11 |
Evaluate Business Approach | 4 days | 20/01 | 23/01 | ||
|
12 |
Define new entity requirements | 1 day | 20/01 | 20/01 | 10 | Manager |
|
13 |
Identify on-going business purchase opportunities | 1 day | 21/01 | 21/01 | 12 | Manager |
|
14 |
Research franchise possibilities | 1 day | 22/01 | 22/01 | 13 | Manager |
|
15 |
Summarize business approach | 1 day | 23/01 | 23/01 | 14 | Manager |
|
16 |
Evaluate Potential Risks and Rewards | 7 days | 21/01 | 29/01 | ||
|
17 |
Assess market size and stability | 2 days | 21/01 | 22/01 | 12 | Advisor |
|
18 |
Estimate the competition | 1 day | 23/01 | 23/01 | 17 | Advisor |
|
19 |
Assess needed resource availability | 2 days | 26/01 | 27/01 | 18 | Advisor |
|
20 |
Evaluate realistic initial market share | 1 day | 28/01 | 28/01 | 19 | Advisor |
|
21 |
Determine financial requirements | 2 days | 26/01 | 27/01 | 15 | Advisor |
|
22 |
Review personal suitability | 1 day | 28/01 | 28/01 | 21 | Manager |
|
23 |
Evaluate initial profitability | 1 day | 29/01 | 29/01 | 22 | Manager |
|
24 |
Review and modify the strategic plan | 2 days | 30/01 | 02/02 | 23 | |
|
25 |
Confirm decision to proceed | 0 days | 02/02 | 02/02 | 24 | |
|
26 |
Phase 2 – Define the Business Opportunity | 27 days | 03/02 | 10/03 | ||
|
27 |
Define the Market | 13 days | 03/02 | 19/02 | ||
|
28 |
Access available information | 1 day | 03/02 | 03/02 | 25 | Advisor |
|
29 |
Create market analysis plan | 2 days | 04/02 | 05/02 | 28 | Advisor |
|
30 |
Implement market analysis plan | 5 days | 06/02 | 12/02 | 29 | Advisor |
|
31 |
Identify competition | 2 days | 13/02 | 16/02 | 30 | Advisor |
|
32 |
Summarize the market | 2 days | 17/02 | 18/02 | 31 | Advisor |
|
33 |
Identify target market niche | 1 day | 19/02 | 19/02 | 32 | Advisor |
|
34 |
Identify Needed Materials and Supplies | 7 days | 20/02 | 01/03 | ||
|
35 |
Select a business approach (from “Evaluate Business Approach” above) | 2 days | 20/02 | 23/02 | 28SS, 33 | Manager |
|
36 |
Identify management staff resources | 1 day | 24/02 | 24/02 | 35 | Manager |
|
37 |
Identify staffing requirements | 1 day | 25/02 | 25/02 | 36 | Manager |
|
38 |
Identify needed raw materials | 1 day | 26/02 | 26/02 | 37 | Manager |
|
39 |
Identify needed utilities | 1 day | 27/02 | 27/02 | 38 | Manager |
|
40 |
Summarize operating expenses and financial projections | 1 day | 01/03 | 01/03 | 39 | Manager |
|
41 |
Evaluate Potential Risks and Rewards | 6 days | 02/03 | 09/03 | ||
|
42 |
Assess market size and stability | 2 days | 02/03 | 03/03 | 40 | Manager |
|
43 |
Assess needed resources availability | 2 days | 04/03 | 05/03 | 42 | Manager |
|
44 |
Forecast financial returns | 2 days | 08/03 | 09/03 | 43 | Accountant |
|
45 |
Review and modify the business opportunity | 1 day | 10/03 | 10/03 | 44 | |
|
46 |
Confirm decision to proceed | 0 days | 10/03 | 10/03 | 45 | Advisor, Peers, Lawyer, Accountant |
|
47 |
Phase 3 – Plan for Action | 21 days | 11/03 | 08/04 | ||
|
48 |
Develop Detailed 5-Year Business Plan | 21 days | 11/03 | 08/04 | ||
|
49 |
Describe the vision and opportunity | 1 day | 11/03 | 11/03 | 46 | Advisor |
|
50 |
List assumptions | 1 day | 12/03 | 12/03 | 49 | Advisor |
|
51 |
Describe the market | 1 day | 15/03 | 15/03 | 50 | Advisor |
|
52 |
Describe the new business | 1 day | 16/03 | 16/03 | 51 | Advisor |
|
53 |
Describe strengths, weaknesses, assets and threats | 1 day | 17/03 | 17/03 | 52 | Advisor |
|
54 |
Estimate sales volume during startup period | 1 day | 18/03 | 18/03 | 53 | Advisor, Accountant |
|
55 |
Forecast operating costs | 1 day | 19/03 | 19/03 | 54 | Advisor, Accountant |
|
56 |
Establish pricing strategy | 1 day | 22/03 | 22/03 | 55 | Advisor |
|
57 |
Forecast revenue | 1 day | 23/03 | 23/03 | 56 | Advisor |
|
58 |
Summarize pro-forma financial statement | 2 days | 24/03 | 25/03 | 57 | Advisor |
|
59 |
Develop break-even analysis | 1 day | 26/03 | 26/03 | 58 | Advisor |
|
60 |
Develop cash-flow projection | 1 day | 29/03 | 29/03 | 59 | Advisor |
|
61 |
Identify licensing and permitting requirements | 1 day | 30/03 | 30/03 | 60 | Advisor |
|
62 |
Develop startup plan | 2 days | 31/03 | 01/04 | 61 | Advisor |
|
63 |
Develop sales and marketing strategy | 1 day | 02/04 | 02/04 | 62 | Advisor |
|
64 |
Develop distribution structure | 1 day | 05/04 | 05/04 | 63 | Advisor |
|
65 |
Describe risks and opportunities | 2 days | 06/04 | 07/04 | 64 | Advisor |
|
66 |
Publish the business plan | 1 day | 08/04 | 08/04 | 65 | Advisor |
|
67 |
Confirm decision to proceed | 0 days | 08/04 | 08/04 | 66 | Advisor |
|
68 |
Phase 4 – Proceed With Startup Plan | 53 days | 09/04 | 22/06 | ||
|
69 |
Choose a location | 1 day | 09/04 | 09/04 | 67 | |
|
70 |
Establish Business Structure | 24 days | 12/04 | 13/05 | ||
|
71 |
Choose a Name | 2 days | 12/04 | 13/04 | ||
|
72 |
Identify implications | 1 day | 12/04 | 12/04 | 69 | Lawyer |
|
73 |
Research name availability | 1 day | 13/04 | 13/04 | 72 | Lawyer |
|
74 |
Choose a Bank | 5 days | 14/04 | 20/04 | ||
|
75 |
Establish accounts | 4 days | 14/04 | 19/04 | 73 | Banker |
|
76 |
Establish line of credit | 1 day | 20/04 | 20/04 | 75 | Banker |
|
77 |
Choose legal representation | 1 day | 21/04 | 21/04 | 75SS, 76 | Lawyer |
|
78 |
Select business tax-basis category | 2 days | 22/04 | 23/04 | 77 | Lawyer, Accountant |
|
79 |
Choose capital funding source | 2 days | 26/04 | 27/04 | 78 | Manager |
|
80 |
Commit capital funding | 0 days | 27/04 | 27/04 | 79 | Manager |
|
81 |
Establish the Operating Control Base | 12 days | 28/04 | 13/05 | ||
|
82 |
Choose and set up the accounting system | 2 days | 28/04 | 29/04 | 79, 80 | Accountant |
|
83 |
Obtain required licenses and permits | 4 days | 30/04 | 05/05 | 82 | Lawyer, Government agency |
|
84 |
Obtain needed insurance | 4 days | 06/05 | 11/05 | 83 | Accountant |
|
85 |
Establish security plan | 2 days | 12/05 | 13/05 | 84 | Advisor, Lawyer |
|
86 |
Develop Marketing Program | 4 days | 13/04 | 16/04 | ||
|
87 |
Establish an advertising program | 2 days | 13/04 | 14/04 | 73SS | Advisor |
|
88 |
Develop a logo | 1 day | 15/04 | 15/04 | 87 | Advisor, Lawyer |
|
89 |
Order promotional materials | 1 day | 16/04 | 16/04 | 88 | Advisor |
|
90 |
Provide Physical Facilities | 15 days | 14/05 | 03/06 | ||
|
91 |
Secure operation space | 5 days | 14/05 | 20/05 | 85, 89 | Lawyer |
|
92 |
Select computer network hardware | 1 day | 21/05 | 21/05 | 91 | Information services |
|
93 |
Select computer software | 1 day | 24/05 | 24/05 | 92 | Information services |
|
94 |
Establish utilities | 3 days | 25/05 | 27/05 | 93 | Manager |
|
95 |
Provide furniture and equipment | 4 days | 28/05 | 02/06 | 94 | Manager |
|
96 |
Move in | 1 day | 03/06 | 03/06 | 95 | Manager |
|
97 |
Provide Staffing | 40 days | 28/04 | 22/06 | ||
|
98 |
Interview and test candidates | 14 days | 28/04 | 17/05 | 79 | Manager |
|
99 |
Hire staff | 10 days | 18/05 | 31/05 | 98 | Manager |
|
100 |
Train staff | 16 days | 01/06 | 22/06 | 99 | Manager |
|
101 |
Start up the business | 0 days | 22/06 | 22/06 | 96, 100 | Manager |
Business Start-Up Process Items and PMLite mapping
In this section, we choose the Ontario Self Employment Program Business Start-Up Process. This process focuses on the business planning. However in this plan, there are operation plan and implementation plan that implies activities in execution phase and operation management phase.
After the business plan is approved, starters will start-up their businesses based on implementation plan the ultimate goal is to implement an operation that align with the operation plan. You may assume there is a process for business execution and a processes for operation management. Our scope will only do the mapping for the business Planning Process.
For each item inside the process, we identify PM concepts or items that would be useful to help executing the tasks. Some of the items can me a project itself.
Business Plan
|
Business Start Up Process |
PML Tools and Concepts |
|
1. Executive Summary |
requirements analysis, scope |
|
2. Company Description |
requirements analysis, scope |
|
2.1 Business Concept |
requirements analysis, scope |
|
2.2 Products and Services Description (Overview) |
requirements analysis, scope |
|
2.3 Key Management Description and Advisors |
|
|
3. Vision and Mission |
milestone planning, scope |
|
3.1 Vision |
milestone planning |
|
3.2 Mission |
milestone planning |
|
4. Goals and Objectives |
milestone planning |
|
4.1 Year One |
|
|
4.2 Year Two |
|
|
5. Industry Research and Analysis |
requirements analysis |
|
5.1 Industry (Size, Growth, Trends and Outlook) |
|
|
5.2 Influences (Social, Cultural, Political, Economic) |
|
|
5.3 Regulatory Issues (Federal, Provincial, Municipal and Industry) |
|
|
5.4 Opportunity |
requirements analysis |
|
6. Target Market Research and Analysis |
requirements analysis, scope |
|
6.1 Target Market Profile and Analysis |
requirements analysis |
|
6.1.1 Market Segment(s) (Size, Growth, Trends, Outlook and Potential) |
Inherit from 6.1 |
|
6.1.2 Geographic |
Inherit from 6.1 |
|
6.1.3 Customer Profile |
Inherit from 6.1 |
|
6.1.3.1 Demographic |
Inherit from 6.1 |
|
6.1.3.2 Psychographic |
Inherit from 6.1 |
|
6.1.4 Consumer Profile (if applicable) |
Inherit from 6.1 |
|
6.1.4.1 Demographic |
Inherit from 6.1 |
|
6.1.4.2 Psychographic |
Inherit from 6.1 |
|
6.2 Competitive Profile and Analysis |
requirements analysis |
|
6.2.1 Competitors |
Inherit from 6.2 |
|
6.2.1.1 Direct |
Inherit from 6.2 |
|
6.2.1.2 Indirect |
Inherit from 6.2 |
|
6.2.2 Competitive S.W.O.T. Analysis Chart |
Inherit from 6.2 |
|
6.2.3 Competitive Advantage |
Inherit from 6.2 |
|
7. Sales and Marketing Plan |
requirements analysis, milestone planning, work breakdown and activity lists, responsibility assignment matrix, work schedules (and checklist and Gantt charts), PM software, Kick off meetings, commercial PM |
|
7.1 Positioning Plan |
Inherit from 7 |
|
7.2 Products and Services Plan |
Inherit from 7 |
|
7.3 Placement/Distribution Plan |
Inherit from 7 |
|
7.4 Packaging (Products) and/or Bundling (Services) Plan |
Inherit from 7 |
|
7.5 Pricing Plan |
Cost management |
|
7.6 Promotion Plan |
Inherit from 7 |
|
7.6.1 Advertising |
Inherit from 7 |
|
7.6.2 Promotion |
Inherit from 7 |
|
7.6.2.1 Customer Promotion |
Inherit from 7 |
|
7.6.2.2 Consumer Promotion |
Inherit from 7 |
|
7.6.3 Publicity Plan |
Communication management |
|
7.6.3.1 Media Relations |
Communication management |
|
7.6.3.2 Trade Relations |
Communication management |
|
7.6.3.3 Public Relations |
Communication management |
|
7.7 Networking Plan |
Communication management |
|
7.8 Sales Plan and Forecast |
Cost management |
|
7.8.1 Sales Plan |
Cost management |
|
7.8.2 Year One Sales Forecast |
Cost management |
|
7.8.2.1 Notes and Assumptions (Incl. Seasonality) |
Cost management |
|
7.8.3 Year Two Sales Forecast |
Cost management |
|
7.8.3.1 Notes and Assumptions (Incl. Seasonality) |
Cost management |
|
7.8.4 Year One Sales Forecast and Promotion Plan Chart |
Cost management |
|
7.8.5 Year Two Sales Forecast and Promotion Plan Chart |
Cost management |
|
|
|
|
8. Operations Plan |
milestone planning, work breakdown and activity lists, responsibility assignment matrix, work schedules (and checklist and Gantt charts), PM software, Kick off meetings, commercial PM |
|
8.1 Legal Name and Trade Name (if different from legal name) of Business |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.2 Legal Structure of Business |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.3 Business Coordinates |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.3.1 Business Address |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.3.2 Telephone Number(s) |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.3.3 Fax Number(s) |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.3.4 E-Mail Address |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.3.5 Website Address |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.4 Business Processes |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.5 Equipment |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.6 Suppliers |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.7 Management Plan, Policies and Procedures |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.7.1 Administrative Plan, Policies and Procedures |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.7.2 Personnel Plan, Policies and Procedures |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.7.3 Quality Control Plan, Policies and Procedures |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.7.4 Customer Service Plan, Policies and Procedures |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.7.5 Payment Plan, Policies and Procedures |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.7.5.1 Suppliers |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.7.5.2 Customers |
Inherit from 8 |
|
8.7.6 Other Management (e.g. Sales, Financial) Plans, Policies and Procedures |
Inherit from 8 |
|
|
|
|
9. Risk Plan |
Risk management, work breakdown and activity lists, responsibility assignment matrix, work schedules (and checklist and Gantt charts), PM software, Kick off meetings, commercial PM |
|
9.1 Risk Assessment and Plan Chart |
Inherit from 9 |
|
|
|
|
10. Implementation Plan |
milestone planning, work breakdown and activity lists, responsibility assignment matrix, work schedules (and checklist and Gantt charts), PM software, Kick off meetings, commercial PM |
|
10.1 Implementation Plan (first three months) Chart |
Inherit from 10 |
|
|
|
|
11. Financial Plan |
cost management |
|
11.1 Start-Up Costs |
cost management |
|
11.2 Sources of Funding |
cost management |
|
11.3 Year One Projected Profit/Loss Statement |
cost management |
|
11.3.1 Notes and Assumptions |
cost management |
|
11.4 Year Two Projected Profit/Loss Statement |
cost management |
|
11.4.1 Notes and Assumptions |
cost management |
|
11.5 Year One Projected Cash Flow Statement |
cost management |
|
11.5.1 Notes and Assumptions |
cost management |
|
11.6 Year Two Projected Cash Flow Statement |
cost management |
|
11.6.1 Notes and Assumptions |
cost management |
|
11.7 Breakeven Analysis |
cost management |
From the above table, we have mapped project management Lite items into business start-up process. There are lots we can use about project management into our business start-up. For example communication management and client requirement are needed when we talk about networking, sales, or even marketing.
For operation management and implementation, we need to use work schedule, work breakdown structure, Gantt chart, tracking, monitoring, activity lists, PM software to help delivering our jobs.
For sales, pricing, financial plan, we can use cost management tools to forecast, plan, track, report, monitor our financial and sales activities.
For risk management plan, we will leverage PM risk management techniques and tools such as risk register, impact and probability tool, risk identification, risk response planning, risk monitoring etc.
For the business description, identifying the business idea, we can focus on using milestones, visions defining techniques.
PM Tools Generation Examples
Of course the mapping is not enough. We need to use it. SO how can we use project management? We can develop tools and practices for ourselves and can stick using them.
There are many tools you can develop and you can use, and many tools have been developed. Tools can be spread sheets, checklist, application, document etc. You can be as creative as you need. The whole point here is to use them. For this article, I will use one of my self-created tools to track my activities.
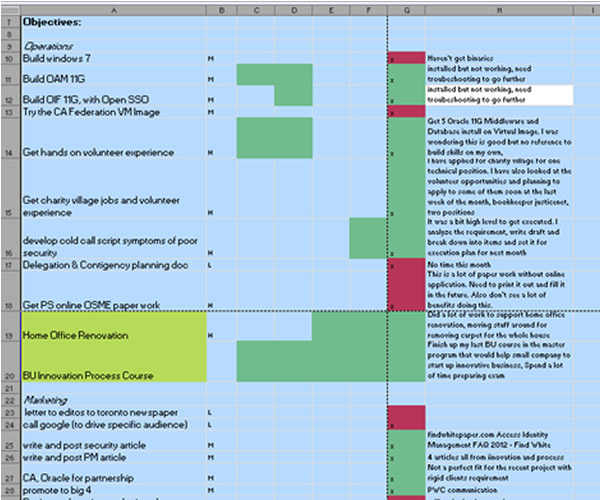
Above is a snapshot of one of the tools. This is to identify, schedule, track, prioritize and report my business start-up activities during my project execution phase. This is rather simple, simpler than project office work breakdown structure and Gantt chart. It does not have duration and dependencies. From the left there are activity lists or work breakdown. Then it has priority for execution. On the next following column, it identifies the tasks should be executed in which during the month. After the tasks have finished you fill the box green. Yellow for in progress and red for not finished. On the far right column you put comments and status update of the item. This can be served as an issue log. Also you can extract this column and the first work item column for monthly reporting. I found this tool handy and it is very easy to make and use. The most important thing is to create a habit of using it and stick to your plan.
Conclusion and Future Work
This article introduces how business starters can use project management to start up their small businesses. First we identify the minimal set of tools that is good enough for small business starters to use. Then we map the project management tools to our business start-up process to identify opportunities we can exploit project management. Finally we can create or borrow tools that adhere to the process mapping. There are lots of work can be done in the future for this program, including educating the public basic project management concepts, introducing or creating project management tools to the user and ensure they develop habit of using them.
The Author
Eric Tse is an international recognized expert/consultant in Enterprise Access and Identity Management Architecture Design and Implementation. He has been working with international renowned experts in information technology in many prestigious companies. He also pursues research interests in project management, financial models, application/enterprise/solution architectures, compilation technology and philosophy of science.
Copyright Project Perfect
